India is a country of diversity and one of the most culturally rich nations in the world. With a population of over 1.3 billion people, India is home to numerous languages that are spoken by its people. The Indian Constitution recognizes 22 languages as official languages of the country, which include Hindi, English, Tamil, Bengali, and Gujarati, among others. In addition to these official languages, there are over 1,600 other languages spoken in India, making it one of the most linguistically diverse countries in the world.
Indian languages are not just a means of communication; they are an important part of the country's cultural heritage. Each language has its unique history, literature, and art, which reflects the diversity of the Indian culture. In this article, we will discuss the history and evolution of Indian languages, their classification, and their importance in Indian culture.
History and Evolution of Indian Languages
The origin of Indian languages can be traced back to the ancient civilization of the Indus Valley, which existed around 4,500 years ago. The Indus Valley civilization had its unique script, which is still a mystery to the linguists. However, the earliest written records of Indian languages are found in the Vedas, the ancient Hindu scriptures that were written in Sanskrit.
Sanskrit is considered to be the mother of all Indian languages and is one of the oldest languages in the world. It is the language of the Vedas, the Upanishads, and many other ancient Hindu texts. The word Sanskrit means "perfected" or "refined," and it is believed that it was created by the sages of ancient India to be a language of clarity and precision. Sanskrit was the language of the elite and was used for religious and philosophical purposes.
Over time, different dialects of Sanskrit emerged, which eventually gave rise to the Prakrit languages. Prakrit is a group of vernacular dialects that evolved from Sanskrit and was spoken by the common people. The Prakrit languages were used in literature, drama, and poetry and were also used in everyday conversations.
During the medieval period, India witnessed the emergence of many regional languages. These languages were influenced by Sanskrit and Prakrit, as well as by the local dialects of the regions. Many of these languages, such as Tamil, Telugu, and Kannada, have their unique scripts and literature.
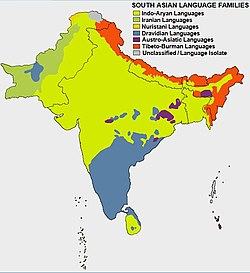
Classification of Indian Languages
Indian languages are classified into four major language families: Indo-European, Dravidian, Austroasiatic, and Tibeto-Burman. Let us take a closer look at each of these language families.
Indo-European Languages: The Indo-European language family is the largest language family in the world and includes over 400 languages. The Indo-European languages are spoken in many parts of the world, including Europe, Iran, and the Indian subcontinent. The major Indo-European languages spoken in India are Hindi, Bengali, Marathi, Punjabi, Gujarati, and Urdu.
Dravidian Languages: The Dravidian language family is mainly spoken in South India and Sri Lanka. The Dravidian languages include Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam.
Austroasiatic Languages: The Austroasiatic language family is spoken in parts of India, Bangladesh, and Southeast Asia. The major Austroasiatic languages spoken in India are Santali, Khasi, and Mundari.
Tibeto-Burman Languages: The Tibeto-Burman language family is spoken in the northeastern part of India and includes languages such as Assamese and Bodo.
Importance of Indian Languages in Indian Culture
Indian languages are an integral part of Indian culture and have played a crucial role in shaping



0 Comments